NEWS
Fiscal Year (FY) 2019 Funding Plan
The NIAMS is operating under the FY 2019 Department of Defense and Labor, Health and Human Services, and Education Appropriations Act. The interim funding plan for research and training grants represents the most current information as of June 25, 2019.
RFI on the NIAMS Strategic Plan for Fiscal Years 2020-2024
Every five years since 2006, NIAMS has released successive Long-Range Plans to help guide the research the Institute supports. Based on public comments received from a previous Request for Information (RFI, NOT-AR-19-009 issued in September 2018), input through listening sessions with the community, and feedback from the NIAMS Advisory Council and its Working Group for the Strategic Plan, NIAMS has drafted a Strategic Plan for Fiscal Years 2020-2024, which is expected to be released this fall.
We have issued a second RFI to seek input on this draft from researchers in academia and industry, health care professionals, patient advocates and health advocacy organizations, scientific or professional organizations, Federal agencies, and other interested members of the public. This RFI is open through July 12, 2019.
Please take a moment to review our current draft of the Strategic Plan (PDF - 1.49MB). I encourage your feedback and comments. Responses may be submitted via an online form by July 12, 2019.
New Clues on Tissue Damage Identified in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lupus
Research supported by the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) Accelerating Medicines Partnership on Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus provides new insights into tissue damage for these autoimmune conditions. Findings include the identification of novel molecular signatures related to immune system signaling in kidney cells that may reflect their active role in disease process; molecular targets, including specific white blood cells, for potential treatment in lupus nephritis; and specific types of fibroblasts and white blood cells that are involved in rheumatoid arthritis. These discoveries set the stage for uncovering potential drug target candidates that could advance to experimental treatments. Results of the studies were published June 18, 2019, in three papers in Nature Immunology.
Dermatology Branch at NIH: Research, Colleagues and a Shift From NCI to NIAMS
The Dermatology Branch has moved from the National Cancer Institute (NCI) to the NIAMS. The Branch conducts clinical and basic investigations of skin biology and researches the etiology, diagnosis and treatment of skin disease in labs located in the NIH Clinical Center. Research areas include the skin as an immunological organ, inflammatory diseases, the human microbiome, skin stem cells and cutaneous malignancies. The Branch conducts clinical studies, provides consultative services in the NIH Clinical Center and trains physicians/scientists in investigative dermatology. Learn more.
Former NIAMS Director Dr. Katz Remembered
Music flowed from Masur Auditorium as more than 400 people gathered on May 3 to celebrate the life of Stephen I. Katz, M.D., Ph.D., former NIAMS Director. The memorial event featured NIH Director Francis S. Collins, M.D., Ph.D., two former NIH Directors and several past and present Institute leaders. Dr. Katz’s three children also spoke at the event.
FDA Approves First Treatment for Pediatric Patients With Lupus
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved Benlysta (belimumab) intravenous infusion for treatment of children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) – often referred to as simply “lupus” – a serious chronic disease that causes inflammation and damage to various body tissues and organs. This is the first time that the FDA has approved a treatment for pediatric patients with SLE. Benlysta has been approved for use in adult patients since 2011.
Other News From FDA
- FDA Approves Innovative Gene Therapy To Treat Pediatric Patients With Spinal Muscular Atrophy, a Rare Disease and Leading Genetic Cause of Infant Mortality
- FDA Permits Marketing of First Diagnostic Test To Aid in Detecting Prosthetic Joint Infections
RESOURCES
Spotlight on Scientific Imagery: Mouse Osteocyte
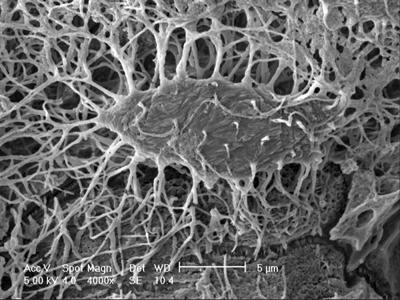
When bone cells called osteocytes sense mechanical stress on the skeleton due to activities such as weight-lifting or even walking, they transform the forces into biological responses, which signal other cells to make or remove bone. Many researchers studying osteocytes also believe that they produce factors that transmit information to other organs and tissues.
Photo credit: Lynda Bonewald, Ph.D., University of Missouri, Kansas City
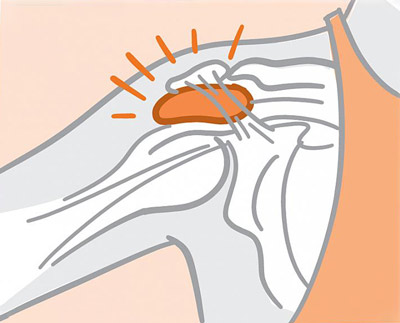
Beating Bursitis: Take Care of Your Joint Cushions
Almost everyone has joint pain at some point in life. It can flair up suddenly. Or, it can start off mild and get worse over time. Treatment for most simple cases of joint pain is similar no matter what’s causing it. This may include rest, over-the-counter drugs that suppress inflammation and gentle stretching and strengthening exercises.
Explore New Social Media Tools From NIAMS
Social media can be a powerful way to reach your target audiences. Check out the new NIAMS Social Media Resources page for effective health messages related to bones, joints, muscles and skin to share with your community.
Now it’s even easier to use social media to positively influence the people in your community to take practical steps toward a healthy lifestyle. The page, available in English and Spanish, features a carousel of shareable graphics and content that link people to reliable health information from the NIAMS. Simply scroll through the content options, choose the graphic you want and click “share this” to post it on your favorite social media channels.
EVENTS
June NIAMS Advisory Council Meeting Available on Videocast
A video recording of the June 5, 2019, NIAMS Advisory Council Meeting is available. The next NIAMS Advisory Council Meeting will be held September 10, 2019.

2019 NIH & FDA Glycoscience Research Day
July 8, 2019
Natcher Conference Center, NIH Campus, Bethesda, MD
NIH Wednesday Afternoon Lecture Series
The NIH’s Wednesday Afternoon Lecture Series offers weekly lectures every Wednesday at 3 p.m. in Masur Auditorium, Building 10, NIH Campus. Renowned scientists from around the globe present research on a variety of topics. The lectures are Continuing Medical Education-certified, open to the public and available live via webcast.
NIH Science Lectures and Events Available via Internet
The NIH hosts a number of science seminars and events that are available online through real-time streaming video (videocast). The NIH calendar notes these videocast events with a video icon ![]() .
.